Description; what is aluminum and magnesium alloy die casting? Learn the different types of metals we can use in casting as well as die casting advantages and disadvantages.
Die casting of aluminum alloys and magnesium alloy. Which alloys are better?
Depending on the technical and operational requirements for products, various grades of aluminum or alloys of several components are used:
1.ADC6:Cu≤0.1,Si≤1.0,Mg2.5~4.0,Zn≤0.4,Fe≤0.8,Mn0.4~0.6,Ni≤0.1,Sn≤0.1,Pb≤0.1,Ti≤0.2.
2.ADC10: Cu2.0~4.0, Si7.5~9.5, Mg≤0.3,Zn≤1.0,Fe≤0.9,Mn≤0.5,Ni≤0.5,Sn≤0.3。
3:ADC12: Cu1.5~3.5, Si9.6~12.0, Mg≤0.3, Zn≤1.0, Fe≤1.3, Mn≤0.5, Ni≤0.5, Sn≤0.3, Ca≤200ppm, Pb ≤0.1, Cd ≤0.005。
4: A380:Cu3.0~4.0;Si7.5~9.5;Mg≤0.1Max;Fe≤1.3Max;Zn≤3.0Max;Mn≤0.5Max;Ni≤0.5Max;Sn0.35Max
A very strong alloy is widely used in aircraft construction. It is suitable for the manufacture of parts of complex devices. Due to its low plasticity, it is not suitable for creating parts of mechanisms subject to constant vibration.
5: Magnesium Alloy AZ91D: Al 8.5-9.5, Zn 0.45-0.9, Mn 0.17-0.40, Si 0.08max , Fe 0.004 , Ni 0.001 , Cu 0.025 , Be 0.0005-0.0015
Aluminum die casting in examples
Die casting is used to create serial products in molds. The casting method is used to manufacture parts for power tools, engines and car bodies, high-precision instruments for the medical industry and food production.
The technology of die casting is as follows:
1. Aluminum is melted in a special induction furnace at a temperature of 660 ° C.
2. The molten mass is fed into the mold under pressure up to 700 MPa.
3. After the product has cooled down, the molds are opened and the product is pulled out.
The entire production cycle can last from a few seconds to tens of minutes, depending on the dimensions of the product.
It is important to choose the right temperature for melting. Exceeding the permissible temperatures can lead to a change in the internal structure of the metal, and insufficient heating will lead to under filling.
But why use an alloy instead of pure metal?
To answer this question it is necessary to analyze the physical, mechanical and microstructural characteristics of an alloy. The union of different elements in fact affects fundamental properties in the metallurgical industry. Such as resistance to corrosion, electrical conductivity, toughness and point breaking.
Furthermore, by using an alloy it is possible to lower the melting point of the metal, thus saving energy destined for heating the furnaces and limiting the erosion of the crucible.
The alloys also offer the possibility to choose, within certain limits, the chemical composition, the most suitable microstructure for the solidification method and for the operations following the casting process.
The choice will also depend on the type of component to be produced, taking into account the required performance characteristics. Among these we remember:
- Pressure seal;
- Corrosion resistance;
- Surface finish;
- Dimensional accuracy;
- Wear resistance;
No less important, however, are the production requirements: when dealing with die-casting metals in a hot chamber, the following three main factors must be taken into account.
- Fluidity
With fluidity we indicate that technological characteristic of an alloy that measures its ability to flow in a mold by filling thin thicknesses. It is defined as a technological characteristic because it depends on both the material and the characteristics of the process, in particular on the solidification and heat exchange with the mold. - Hot Crack Resistance
This term indicates the ability of an alloy to withstand stresses due to shrinkage during cooling and solidification. - Shrinkage due to solidification
This characteristic affects the possibility of forming porosity and cracks in the die-cast.
In particular, alloys resistant to hot cracking are particularly suitable for some rapid processes such as hot chamber die casting, while low-cost alloys can be used without problems.
There are 3 main types of zinc diecasting alloys:
- ~ 4% Aluminum alloys;
- 8-27% Aluminum alloys;
- Proprietary alloys;
For each of these groups there are products with different percentages of secondary metals. The most suitable alloys for hot chamber die casting are Zamak 3, 2, 5 and 8: these are alloys with an aluminum percentage ranging from 2.5% to 28%.
The presence of aluminum in zinc alloys has three main reasons:
first of all, it reduces the melting point of the alloy, decreasing the amount of thermal energy used by the machinery, offering energy savings. Moreover it also reduces the aggressiveness of the alloy towards steel. The material of which the siphon, the crucible and the mold are made.
Thus extending the life of these tools; finally it increases the fluidity of the alloy allowing to obtain smaller thicknesses and to facilitate the molding. If the alloy loses aluminum, its castability also decreases, increasing the risk of hot cracking and sticking in the mold.
Copper as an Alloy
Copper is the third component in the alloy, with quantities ranging from 0% to 3.5%. Unlike aluminum which is always present, the quantity of copper can be zero. This is because despite the presence of copper it increases the mechanical characteristics, hardness and wear resistance, at the same time it decreases the percentage elongation at break and the toughness of the alloy.
In addition, it can cause dimensional instability: this means that the jet tends to increase in size over time.
The behavior of magnesium is similar to that of copper
It can be an advantage or a disadvantage. Depending on the cases and the doses it can therefore be considered part of the alloy or an impurity. For example, it can be added to the alloy to counteract the effects of intergranular corrosion.
But it has a strong negative impact on castability if it exceeds 0.05%. Other effects related to the presence of magnesium are increased alloy hardness, increased risk of hot cracking and other surface finish problems.
At this point it should be evident that even small percentages of foreign components can have a great influence on the results obtained by die casting, and not always positive.
In the following table you will find a list of contaminants and their influence on the diecast:
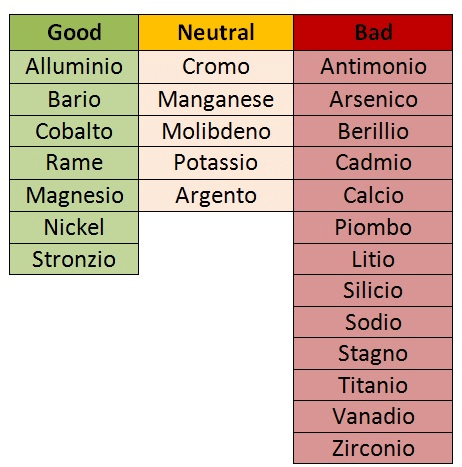
It is therefore essential to carry out checks on the raw material purchased, in order to avoid discovering when production was started that the formation of defects in die castings simply depended on small percentages of foreign metals infiltrated into the raw material.
What should be noted when using metal for Die Casting?
In order to select the right metal to use for the die casting process, technicians must rely on the function of the Die Casting process, the actual production process and the products created to determine exactly.
For example, when testing to select the right metal for the Die Casting process, for products that have high requirements for surface strength and effective corrosion resistance, from this requirement, the technique is used.
The staff will choose copper metal or other alloys to conduct extrusion molding the most suitable product, giving the best product quality when used.
Moreover, in the process of manufacturing products, engineers need to have an exchange about the most suitable volume, product curing properties, effective materials, long life, and good durability.
We need to choose zinc metal instead of copper, increase the life of the product by 10 times if you choose copper to extrude the product during the Die Casting process!
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Die Casting?
What advantages and disadvantages does Die Casting bring in the application process for product die casting in the field of current molding techniques? As follows:
What are the advantages of Die Casting?
The advantages that Die Casting brings are as follows:
Firstly, bringing different dimensional strength, in the die casting process, products using Die Casting will have much stronger features than using that plastic!
Secondly, the production process will go faster thanks to Die Casting, easy to conduct die casting with large volume and without too many tools, it does not take much time to process products, from which results in better production efficiency and product quality.
Third, the surface of the products made from Die Casting will be smoother. The curvature is suitable, there will be no worries about the unsafe angle issues when using. The product is strongly connected and brings high quality and greater efficiency in the human use of the product.
Fourth, the product created will be more accurate thanks to Die Casting. Applying advanced technical parameters brings products to the right design, creating perfection and satisfaction for customers in the process of using the product.
What are the disadvantages of Die Casting?
Besides the advantages, Die Casting also has some disadvantages as follows:
Firstly, when implementing Die Casting into the production of products, it is possible to reduce the cost efficiency. But the efficiency of the product is significantly reduced due to the high volume.
Secondly, the alloys are easy to change. The mobile metals are limited when using Die Casting in the production process, after finishing. And the shape of the product is also quickly changed when there is an impact motion.
Third, products created from Die Casting will be limited in weight and size.
Fourth, in the process of Die Casting, many variations of products may appear. Such as: A mold is only used for one product and cannot be cast for other products. From there, many different molds must be created to serve the molding of products in the Die Casting process.
Thus, you can see that, Die Casting has both advantages and disadvantages, mechanical engineers need to know how to use it effectively to bring applicability and high quality in their work.
